How to operate a drone is a question many beginners ask. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll explore everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, whether you’re a novice or looking to enhance your existing skills.
This detailed exploration will cover essential topics, ensuring a smooth and safe flight experience every time.
From understanding the intricate workings of a drone’s various components to navigating the complexities of flight modes and GPS usage, this guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions. We will also delve into the crucial aspects of legal compliance and responsible drone operation, equipping you with the knowledge to fly safely and legally. Furthermore, we’ll address common troubleshooting issues and provide essential maintenance tips to ensure your drone’s longevity.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will Artikel the key parts of a typical drone and provide a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated work of several key components. Let’s examine each one:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, move, and hover. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are commonly used in modern drones for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this sophisticated computer processes data from various sensors (gyroscope, accelerometer, barometer, GPS) to maintain stability and execute pilot commands.
- Battery: Provides power to all drone components. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are frequently used due to their high energy density and lightweight nature. Proper battery care is essential for safety and performance.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and navigation. Crucial for features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and waypoint navigation.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each individual motor, allowing for precise control of the drone’s movement and stability.
- Gimbal (for camera drones): A stabilized mounting system for the camera, ensuring smooth and steady footage, even during flight maneuvers.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements remotely.
- Receiver: Receives signals from the transmitter and relays them to the flight controller.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms is essential for understanding manuals, online resources, and discussions with other drone enthusiasts.
- Altitude Hold: Maintaining a constant height above the ground.
- Gimbal Lock: A situation where the gimbal’s freedom of movement is restricted.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated function that guides the drone back to its starting point.
- Waypoint: A pre-programmed location that the drone will navigate to.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s vertical movement (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right (sideways).
- LiPo Battery: Lithium Polymer battery, a common type of battery used in drones.
- ESC: Electronic Speed Controller, manages motor speed.
Drone Component Troubleshooting
This table summarizes common issues, their potential causes, and troubleshooting steps.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust | Bent or damaged propellers, unbalanced propellers | Inspect for damage, replace damaged propellers, ensure proper balancing |
| Motors | Power propellers | Motor failure, overheating | Check motor connections, allow motors to cool down, consider replacing faulty motors |
| Flight Controller | Controls drone stability and movement | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions | Restart the drone, recalibrate sensors, update firmware |
| Battery | Provides power | Low battery, battery failure | Charge the battery, replace faulty batteries |
| GPS Module | Provides positioning and navigation | Weak GPS signal, GPS failure | Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky, check for obstructions, replace the GPS module if necessary |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount for safe and responsible drone operation. This section details the steps involved in preparing for a flight and maintaining safety.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check the following:
- Battery Check: Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine propellers for damage or imbalance.
- GPS Signal Verification: Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired.
- Controller Connection: Verify that the controller is properly connected to the drone.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone for any damage or loose parts.
- Calibration: If needed, calibrate the compass and IMU.
- Environment Check: Assess the surrounding environment for any potential hazards or obstacles.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure compliance with local regulations and airspace restrictions.
Safety Guidelines
Safe drone operation involves more than just a pre-flight checklist. These guidelines are critical:
- Maintain Visual Line of Sight (VLOS): Always keep the drone within your direct line of sight.
- Avoid Obstacles: Fly away from obstacles such as trees, buildings, and power lines.
- Respect Privacy: Do not fly over private property without permission.
- Adhere to Regulations: Comply with all local, state, and federal drone regulations.
- Fly Responsibly: Do not endanger people or property.
- Be Aware of Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in inclement weather such as strong winds or rain.
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Flowchart
A visual representation of the steps involved in a safe launch and landing process:
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here. The steps would include powering on the drone and controller, calibrating the compass and IMU, checking GPS signal strength, performing a pre-flight check, initiating a safe takeoff, performing the flight maneuvers, and initiating a safe landing sequence, followed by powering off the drone and controller.)
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety regulations. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which can be achieved by consulting a comprehensive guide, such as this one on how to operate a drone. From there, practice is key to mastering the skills needed for safe and effective drone operation.
Ultimately, responsible drone piloting hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic drone controls and maneuvers is fundamental to safe and efficient operation. This section details the functions of control sticks and common maneuvers.
Drone Control Stick Functions
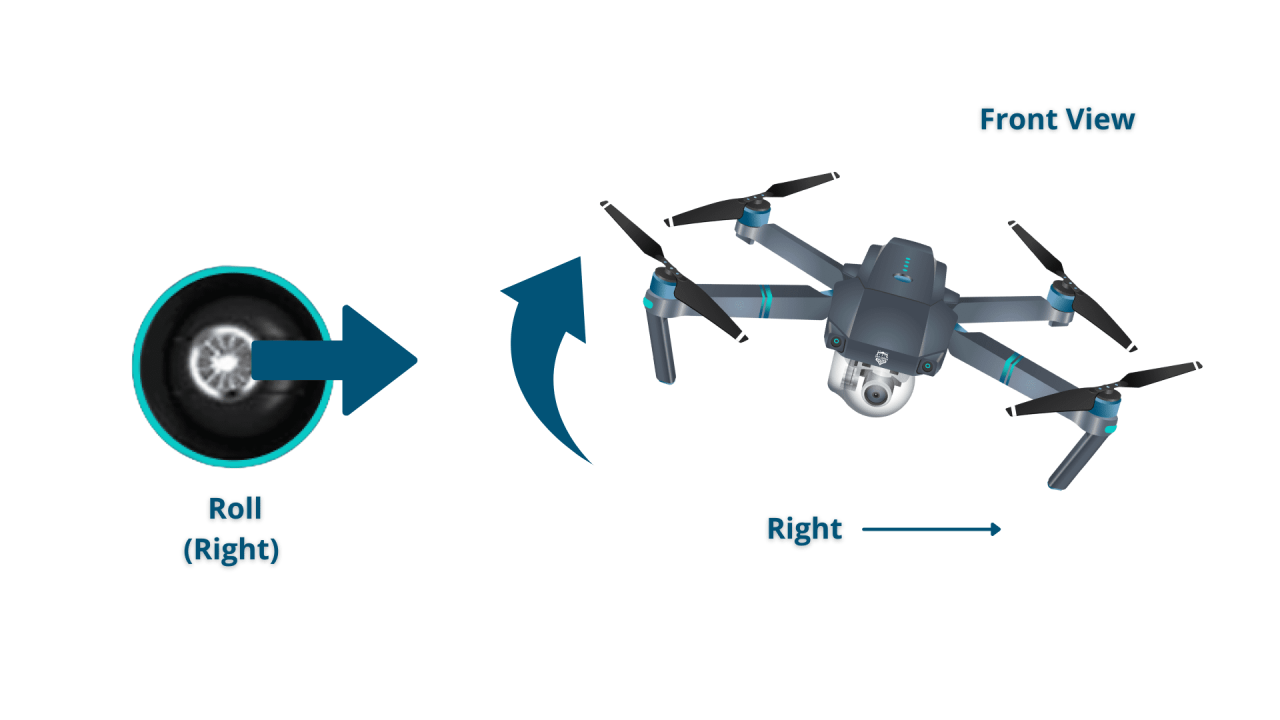
Most drone controllers utilize two sticks to control the drone’s movement:
- Left Stick (Throttle/Pitch): The left stick typically controls altitude (throttle) and forward/backward movement (pitch). Pushing the stick up increases altitude and pushing it forward moves the drone forward.
- Right Stick (Roll/Yaw): The right stick controls left/right movement (roll) and rotation (yaw). Pushing the stick to the right makes the drone roll to the right and pushing it to the left makes it roll to the left. Rotating the stick left or right controls yaw (rotation).
Basic Drone Maneuvers
These maneuvers are the foundation of drone piloting:
Taking Off
- Ensure a strong GPS signal and clear airspace.
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off vertically.
- Maintain a steady hover once airborne.
Hovering
- Maintain a stable altitude and position.
- Use small, precise stick movements to correct for any drift.
- Practice maintaining a steady hover in various conditions.
Moving Forward/Backward/Sideways
- Use the pitch (forward/backward) and roll (sideways) controls on the left and right sticks respectively.
- Maintain a steady altitude while moving.
- Practice smooth and controlled movements.
Landing
- Slowly decrease throttle to descend vertically.
- Maintain control of the drone’s position during descent.
- Perform a gentle landing on a flat, stable surface.
Turning
- Use the yaw control on the right stick to rotate the drone left or right.
- Maintain a steady altitude and position while turning.
- Practice smooth and controlled turns.
Ascending and Descending
- Use the throttle control on the left stick to increase or decrease altitude.
- Maintain a steady position while ascending or descending.
- Practice smooth and controlled ascents and descents.
Understanding Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, catering to different skill levels and flight situations. This section explores common flight modes and their characteristics.
Flight Mode Comparison
Drone flight modes are designed to simplify operation and enhance safety. Let’s compare three common modes:
| Flight Mode | Description | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness, enhances stability. | Easy to learn, suitable for beginners, safer for initial flights. | Limited maneuverability, slower response times. |
| Sport Mode | Increased speed and responsiveness, more aggressive maneuvers. | Enhanced maneuverability, faster response times, more exciting flying experience. | Requires more skill and precision, higher risk of crashes. |
| GPS Mode | Utilizes GPS for position holding and return-to-home functionality. | Improved stability, accurate positioning, automated return to home. | Requires a strong GPS signal, can be affected by GPS interference. |
Navigation and GPS Usage
GPS plays a vital role in drone navigation and stability, offering features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and waypoint navigation. This section explains how to utilize these GPS features effectively.
Importance of GPS for Drone Navigation

GPS provides crucial information for precise positioning and navigation, allowing for stable flight and automated features.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, I highly recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering the basics is crucial before tackling more complex flight patterns; safe and responsible drone operation is paramount.
Return-to-Home (RTH) Functionality
RTH is a safety feature that automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point. This is typically activated via a button on the controller or through a setting in the drone’s app.
Setting Up Waypoints and Automated Flight Paths
Many drones allow users to set waypoints—specific geographical coordinates—to create automated flight paths. This often involves using the drone’s accompanying app or software. The process usually involves selecting points on a map, setting the altitude, and letting the drone autonomously navigate between these points.
Drone Photography and Videography Basics
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding composition, lighting, and stabilization techniques. This section provides tips for enhancing your aerial imagery.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Achieving professional-looking aerial footage requires attention to several key elements:
- Composition: Utilize the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing images.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting conditions.
- Stabilization: Use a gimbal to minimize camera shake and ensure smooth footage.
- Framing: Carefully frame your shots to highlight the subject and create visual interest.
- Focus: Ensure your subject is in sharp focus.
Best Practices for Different Aerial Shots
Different shot types require specific techniques:
- Wide Shots: Capture the overall scene and context.
- Close-Ups: Emphasize details and textures.
- Tracking Shots: Follow a moving subject.
- Aerial Panoramas: Create a wide, sweeping view of the landscape.
- Vertical Shots: Capture details from above.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems

This section identifies common drone malfunctions and provides troubleshooting steps to address them.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, battery degradation | Charge the battery, replace the battery if necessary |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, weak signal, GPS module malfunction | Fly in an open area, check for obstructions, recalibrate GPS, replace the GPS module if necessary |
| Motor Failure | Motor damage, ESC malfunction, loose connections | Inspect motors and ESCs, check connections, replace faulty components |
| Drone Won’t Take Off | Low battery, faulty propellers, software issues | Charge the battery, inspect propellers, restart the drone, update firmware |
| Drone is Unstable | Wind, GPS signal loss, calibration issues | Fly in calm conditions, check GPS signal, recalibrate sensors |
Drone Maintenance and Battery Care
Regular maintenance and proper battery care are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring safe operation. This section details a routine maintenance schedule and battery care procedures.
Routine Drone Maintenance, How to operate a drone
A regular maintenance schedule includes:
- Cleaning: Gently wipe down the drone body and components with a soft, damp cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Pay close attention to the propellers, removing any dirt or debris.
- Inspection: Carefully inspect all components for any damage, loose parts, or wear and tear. Check the propellers for cracks or bends, the motors for any signs of damage, and the battery for any swelling or damage.
- Storage: Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Store the battery separately in a dedicated battery storage case.
Proper Battery Charging and Storage
Proper battery care is essential for safety and longevity:
- Charging: Use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and charging procedures. Avoid overcharging or discharging the battery.
- Storage: Store LiPo batteries at a partially charged state (around 30-50%) in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Never store them fully charged or completely discharged.
- Safety Precautions: Always charge LiPo batteries in a fire-resistant area and never leave them unattended during charging.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for responsible and legal drone operation. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance and provides resources for finding relevant regulations.
Importance of Understanding Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by region and are constantly evolving. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal action, or even criminal charges. It’s crucial to stay updated on the latest rules and regulations in your area.
Examples of Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions often include areas near airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. No-fly zones may also be established temporarily for special events or emergencies. Always check the airspace before flying.
Resources for Finding Drone Regulations
Several resources can help you locate the relevant drone regulations in your area, including the FAA website (for the United States), and equivalent national aviation authorities in other countries. Many online tools also allow you to check airspace restrictions before a flight.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a solid foundation in both areas, equipping you with the confidence to handle your drone safely and effectively. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot. By combining the information presented here with hands-on experience, you’ll be well-prepared to explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography, all while adhering to responsible and legal flight practices.
Happy flying!
Questions Often Asked: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones on the market offer beginner modes and stability features. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. Perform this before each flight, especially if you’ve experienced unusual behavior.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to manual control and attempt to return to your starting point. Many drones have a “Return to Home” (RTH) function, but manual control is important in emergencies.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight time varies significantly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time.
